

The coprimary outcome was failure to rescue, defined as maternal mortality after AFE. Main Outcomes and Measures The primary outcome was clinical, pregnancy, and delivery characteristics of AFE, assessed with a multivariable binary logistic regression model. Objective To examine the clinical, pregnancy, and delivery characteristics and the maternal outcomes related to AFE in a recent period in the US.ĭesign, Setting, and Participants This retrospective cohort study examined hospital deliveries from January 1, 2016, to December 31, 2019, from the Healthcare Cost and Utilization Project’s National Inpatient Sample. Because of the rarity of AFE, associated risks factors and maternal outcomes have been relatively understudied. Importance Amniotic fluid embolism (AFE) is an uncommon pregnancy complication but is associated with high maternal mortality. Shared Decision Making and Communication.Scientific Discovery and the Future of Medicine.Health Care Economics, Insurance, Payment.Clinical Implications of Basic Neuroscience.Challenges in Clinical Electrocardiography.

#Doctors who specialize in amniotic fluid embolism how to#
Hopefully as we continue to do more research, we will be better able to understand why AFE happens in some women and not others, and how to more effectively treat it so those women who do experience one have a better chance at a full recovery. We still have much to learn and understand about AFE. Unfortunately these are all very broad, so it is almost impossible to know who will be affected by an AFE. However, we do know that older women, women who’ve had more babies, have a male fetus, undergo induction of labor, deliver by forceps or vacuum or via C-section, have a placenta previa or abruption, or are a racial minority all increase the risk. It can be hard to predict who will go on to develop an AFE since they are so rare. Injury to the brain (like that seen in stroke patients) can also occur. Transferring the woman to the ICU so she can be closely monitored and treated is critical once she is stabilized.įor women who survive to this point, they still may go on to have injuries to their lungs and have trouble breathing. Managing bleeding with medicines and transfusion is critical as well. The next step in treatment is to quickly start cardiac life support management, which means helping the woman get the oxygen she needs and helping her heart pump blood, usually through chest compressions and sometimes with a defibrillator. Minutes matter, so quick thinking and calling in additional help is the most important step. The treatment for AFE lies in the ability for the obstetric team to first realize what is going on and correctly diagnose it. Hemorrhage is often seen at this time, since the parts of the blood responsible for clotting can no longer do their job. This is often followed by complete cardiovascular collapse, where her heart will often stop beating or beat abnormally. Her blood pressure will also drop dangerously low. If oxygen levels are being monitored, doctors will see her oxygen levels rapidly drop to a dangerous level. She then develops a sudden onset of shortness of breath. In the most simplistic way, you can think of it as the mom having an anaphylactic reaction to her baby’s cells, just as someone who is allergic to peanuts would if they ate a peanut butter sandwich.Īn AFE can look very different in each woman, but the classic picture is a mom who has just given birth (either vaginally or by C-section). In AFE, however, the body goes into overdrive.
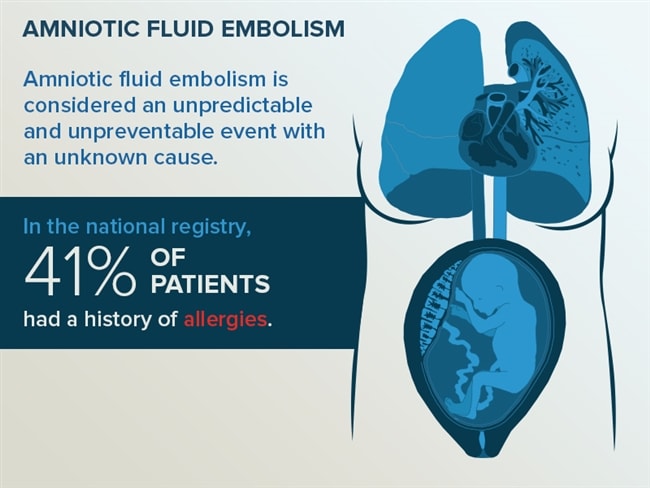
At every delivery there is some mixing of mom and baby’s blood, but most women will not react at all to her baby’s cells being introduced into her blood stream. Here we will break down what it is and how it can be treated.Īn AFE is when a woman has some sort of overactive inflammatory response to her baby’s cells. It only occurs in about 1 in 40,000 deliveries, but it can be deadly, with a 20 to 60 percent mortality rate. An amniotic fluid embolism, or AFE, is thankfully an extremely rare complication of birth.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
